Advantages and Risks of Self-Service Analytics
Self-service analytics is likely to spread in all the business layers, and with proper care to avoid certain risks, the culture of self-service analytics will help all organizations.
Data proliferation has made every business data driven. The impact is, all business is analytics driven and all business users are analytics users. So the major challenge of modern business is how to balance support for self-service analytics while ensuring security and integrity. The purpose of self-service analytics is to empower business users to work with their relevant data independently with little help from IT or BI team. The self-service process can only be made successful with the help of latest BI self-service tools and infrastructure, because the traditional BI tools are not fit for self-service support.
In this article, we will try to explore both sides of self-service analytics and its impact on business. We will also take a look at the future of this trend.
The rise of self-service analytics
Self-service analytics can be defined as a simple form of business intelligence (BI), where business users are empowered to access relevant data, perform queries and generate reports themselves with the help of easy-to-use self-service BI tools. The entire self-service process is simplified or scaled down for better usability.
The purpose of self-service analytics is to enable business users to perform their day-to-day analytics tasks themselves and frees up the BI team (having proper back ground in statistical analysis and data science) to get involved in more critical data analysis process.
As per Gartner's prediction, by 2017, most of the business users will have access to self-service BI tools. But at the same time, one out of ten initiatives will be well-governed with positive business impact. And, the rest will have issues with data inconsistency.
How can we manage the data chaos?
In the modern age of business, organizations need to be more agile in case of new data sources and business requirements. Self-service analytics is a step towards this goal. And, the challenge is how to manage the data chaos while employees are doing self-service analytics.
Following are some pointers which can help us manage the data chaos.
- Introduction of more powerful self-service BI platforms along with the existing BI tools
- Expand the adoption of modern BI tools in each individual business units
- Implement strict governance to ensure data quality and consistency
- Introduce clear roles and responsibilities across the organization
Self-service analytics and ‘citizen data scientist’
Citizen data scientist is a term closely associated with self-service analytics. The idea is, with the help of advanced BI tools and technologies, business users (who does not have proper data science back ground) can perform analytics tasks (self-service analytics). These set of people are known as citizen data scientists, although, people have different opinions with this term. As per Gartner prediction, the number of citizen data scientists will grow five times by the year 2017.
Gartner report defines a citizen data scientist as "a person who creates or generates models that leverage predictive or prescriptive analytics but whose primary job function is outside of the field of statistics and analytics." Alexander Linden, Research Director at Gartner, predicts that through 2017, the number of such "Citizen Data Scientists" will grow 5 times faster than the number of highly skilled Data Scientists.
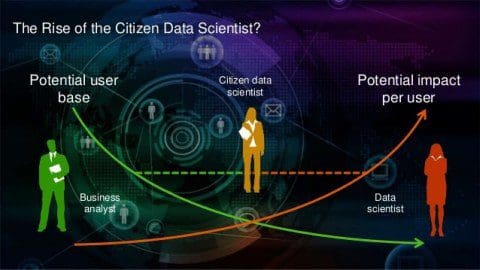
Fig 1: Rise of Citizen Data Scientist,
from Timo Elliott presentation, 2015
Advantages of self-service analytics
Big data and analytics is now an integral part of every organization and their business. It is spreading so rapidly, that the organizations are finding it difficult to manage with limited number of pure data science professionals. Here comes the rise of self-service analytics and citizen data scientists.
Following are some of the advantages.
- Democratize Big Data: Democratization of big data is only possible when it is used by the majority of the users. Self-service analytics is making the path towards this goal. It spreads the awareness among the common users who are actively involved or will be involved in self-service analytics tasks.
- Empower business users: In this age of data explosion, if analytics tasks are confined within a limited set of people, then the organization will not be able to leverage the power of analytics. Self-service analytics empowers the business users to do their tasks themselves.
- Data science team can concentrate on the core analytics tasks: By using self-service analytics, business users can perform less intensive tasks like data exploration, verification, visualization and reporting on their own. As a result, the core data science team can concentrate on more critical and complex tasks. And it gives a lot of value addition to the organization and business.
- Work together for better productivity: Self-service analytics users and core data science team can work together for the best result. Business users can help themselves with self-service, and core data science team can take input from self-service analytics team for further advanced analytics or complex tasks. So it goes together as one single team to achieve a common goal.
Risks of self-service analytics
Every new concept has its own risks, and self-service analytics is not different. Let us try to analyze some of risk factors associated with it.
- Lack of proper training: To implement self-service, the first step is to select right set of people and train them rigorously on self-service BI tools. Lack of proper training can lead to a wrong decision.
- Limitations of business users: Business users also have their own limitations in terms of skills, knowledge, back ground qualification etc. So, an organization has to judge it properly who can do what. And after that, specific trainings should be provided. Otherwise, these limitations can yield negative results.
- Risk of self-service tools: You cannot completely rely on self-service BI tools as these tools can also have errors. So it can be risky, if the results from these tools are not checked and verified properly.
- Data inconsistency: Organizations have to ensure data consistency before implementation self-service in different business layers. Any inconsistency in data can lead to an inconsistent and erroneous output.
- Lack of proper governance: Even after ensuring all the above points, risk is not completely removed unless proper governance is implemented in the entire process. Any loop holes in the governance process can make it a mess.
What is the future?
Big data is going to grow day by day and hence the analytics will rule the business world. So the future is all about big data and analytics in different forms. Now is the time, when the organizations are trying to spread the simple analytics tasks to the business users and leverage the core competency of data science team in more specific areas. So the business, IT and the core data science team will work collaboratively to achieve the common goals of business success.
Summary: Self-service analytics is here to stay and spread gradually in all the business layers. The term 'citizen data scientist' is tied with self-service analytics, and it means the self-service users. May be, the term can be changed to make it more specific and meaningful, as there are lot of debates around it. But the main intention is to identify the benefits and risks of self-service analytics and its future. And, it is clearly visible that the culture of self-service analytics will help all the organizations, if proper care is taken from the management.