 Command Line Basics Every Data Scientist Should Know
Command Line Basics Every Data Scientist Should Know
Check out this introductory guide to completing simple tasks with the command line.
By Rebecca Vickery, Data Scientist
If you are a data scientist or learning data science and want to move beyond using jupyter notebooks to writing production-ready code, the chances are that you will need to use the command line for some tasks. I find that documentation for production data science tools and processes often assume that you already know these basics. However, if you don’t come from a computer science background then it is possible that you won’t know how to complete some of the simpler tasks from the terminal.
I wanted to write this brief guide to the absolute basics of using the command line to perform simple tasks. Knowing some of these basics will undoubtedly make your workflows more efficient and be helpful when working with production systems.
Navigating files and directories
When you open the terminal this is usually what you will see.

The ~ symbol is shorthand for your home directory so this means that you are currently in this directory. If you type the command pwd it will display your present working directory which in our case looks like this /Users/myname.
If you want to create a new directory you can type the following mkdir testthis will create a new directory called test. You can now navigate into this directory using the cd command.
You can also navigate directories by typing .. this will take you back one directory. So in our case, we would go back to the home directory.
Working with files and directories
Next, let’s create a new python file in our test directory. To create a file you type this command touch test.py. This creates a blank python file. The lscommand prints the contents of a directory to the terminal so we can use this to check that our file has been created.
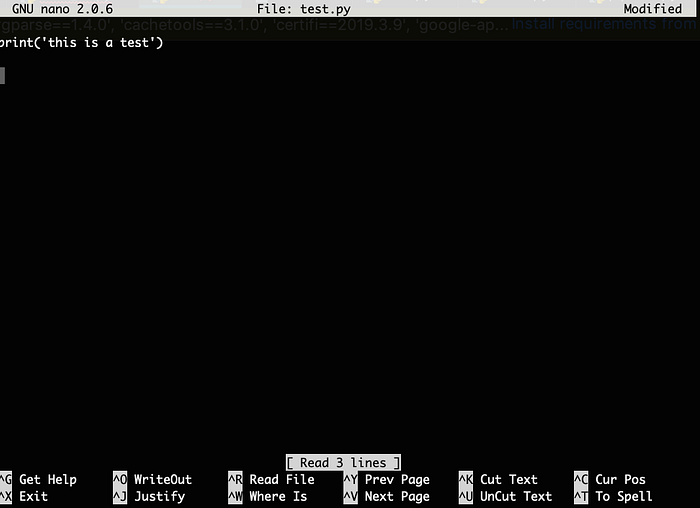
We will edit the file using a program called nano. To open the file you simply type nano test.py and a new tab will open which looks like this.

For this example, we will just make a small change so we will type print('this is a test') . To save the file you can use the shortcut Ctrl+Oand to exit the program Ctrl+X.
Now we have edited the file we can run it using this command python test.py. The simple python code is executed and ‘this is a test’ is displayed on the terminal.

Moving and deleting
Let’s quickly make a new directory mkdir new to explore how to move files. There are three main ways you may want to do this.
The . before the forward-slash (./new) in the commands below is shorthand for the parent directory (test).
- Make a copy and move the copy to retain the original file in the current location
cp test.py ./new - Move the file without copying
mv test.py ./new - Copy the file and rename the file in the new location
cp test.py ./new/test_new.py
Finally, to delete a file we can use rm test.py. To delete an empty directory you can use rmdir new. To delete a directory containing some files rm -rf new.
This post covers some of the most basic tasks a data scientist may need to complete from the command line. If you want to explore some more advanced command-line tools I have written another guide here.
Thanks for reading!
Bio: Rebecca Vickery is learning data science through self study. Data Scientist @ Holiday Extras. Co-Founder of alGo.
Original. Reposted with permission.
Related:
- Five Command Line Tools for Data Science
- Top 12 Essential Command Line Tools for Data Scientists
- Data Science at the Command Line: Exploring Data

 Command Line Basics Every Data Scientist Should Know
Command Line Basics Every Data Scientist Should Know