Create and Deploy your First Flask App using Python and Heroku
Flask is a straightforward and lightweight web application framework for Python applications. This guide walks you through how to write an application using Flask with a deployment on Heroku.
By Divy Shah, Data Scientist.

Prerequisites
Installation
After installing Python, install the other frameworks and libraries listed. You can easily install flask using the following command.
pip install Flask #pip install
Define the structure of your web app
static
|_main.css
template
|_display.html
app.py
trending.py
requirements.txt
The static directory contains your CSS files, and the template contains the HTML file, which is used for rendering.
You can create a separate .py file for your logic and other operations or write code in the same app.py. I suggest creating a separate file will reduce the confusion.
Step 1:
Create your app.py file
I used the waitress service because using this library is meant to be a production-quality pure-Python WSGI server with very acceptable performance. It has no dependencies except ones that live in the Python standard library.
Install waitress
pip install waitress
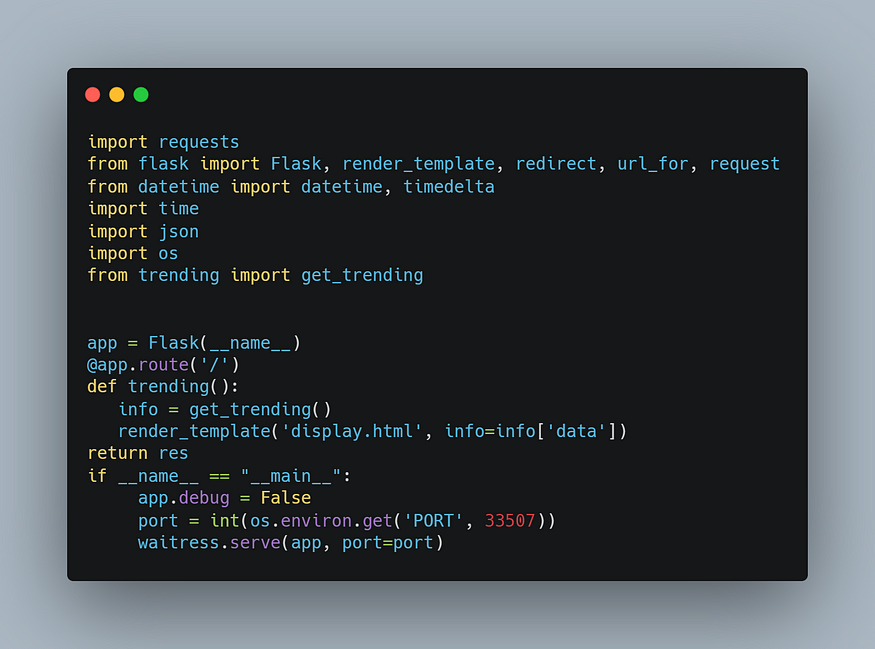
app.py
import requests
from flask import Flask, render_template, redirect, url_for, request
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import time
import json
import os
from trending import get_trending
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def trending():
info = get_trending()
render_template('display.html', info=info['data'])
return res
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.debug = False
port = int(os.environ.get('PORT', 33507))
waitress.serve(app, port=port)
As shown above, we used the GET Method to send data from the server.
There are several other methods also available, which are:
POST: It is used to send user/form-data to the server and doesn’t cache the transmitted data.
HEAD: It is similar to GET, but the difference is it is used without the response body.
PUT: It is used to replace the current resource with uploaded content.
DELETE: It is used to delete the target resource provided in the URL.
Step 2:
Create trending.py file, which is basically the file that contains your business logic. After creation import main function in app.py file.
from trending import get_trending
Below, my trending.py file looks like:

trending.py
After collecting the data, we can render the output using an HTML file.
The output data will be displayed on the HTML page.
Step 3:
Create an HTML file to render the output that you collected from the response object.
Below is how my display.html file looks:

display.html
You are almost done with the coding part, and now it’s time to deploy our first flask app.
Before deploying the app, first, check the flask app on the localhost.
Deployment Steps
1. Login to your Heroku account using CLI
You can log in by writing the following command in the terminal:
heroku login
2. Create a web app on Heroku
You can create a new application on Heroku using the following command:
heroku create < your_app_name >
3. Create requirements.txtfile in the same project directory
To generate the requirement.txt file, you can use the following command”
pip freeze > requirements.txt
4. Create a Procfile
Procfile is a Process file that is required for all Heroku applications. Procfile specifies the commands that are executed by the app on startup.
Click here to read more on Procfile
Enter the following in Procfile:
web: gunicorn app:app
Here, the app is the name of your main (.py) file. In my case, it is app.py.
If you haven’t yet installed the gunicorn web server, then install it by using the following command:
pip install gunicorn
NOTE: you have to create a Procfile without any file extensions.
5. Create runtime.txt to specify the Python version at runtime
After creating a runtime.txt, add your build Python version like below:
python-3.8.1
Now, we are all set!
6. Initialize an empty git repository and push the code
git init
Next, it is time to commit your final code using the following steps:
git add . git commit -m "My first commit" git push heroku master
Your app is live now, and you can see your web app using the generated URL.
Please check out my demo web application at: https://trending-shows.herokuapp.com/
Original. Reposted with permission.
Bio: Divy Shah is passionate about solving real life and FinTech industries problem with the help of Data Science and Machine Learning Algorithms, and is always eager to learn and explore new Data Science algorithms and frameworks.
Related:
