Data Science and Analytics in Personalized Healthcare: Progress and Prospects
Take a glimpse at how the combined capabilities data science, analytics and AI technologies are shaping the present and future of personalized healthcare.

Image by Pexels
Healthcare services are no longer limited to one-size-fits-all approaches applicable to every patient. Instead, there has been a gradual shift towards more individualized and patient-centered solutions. Accordingly, personalized healthcare aims to provide patients with treatments and medical assistance that are tailored to their unique health status, medical history, and lifestyle: simply put, tailored to their associated data.
The explosion in availability and quality of healthcare data together with the rapid progress in data science and analytics methods, have largely contributed to this digital transformation, enabling health professionals to obtain actionable insights by analyzing huge datasets of patient records, clinical data, and even information collected by wearable devices. The result? A dramatic evolution of healthcare systems, which are nowadays capable of performing accurate predictions, identifying risks promptly, and delivering more effective treatments, often underpinned by the power of personalization.
This article examines the role of data science and analytics tools in personalized healthcare, focusing on predictive analytics and the integration of machine learning (ML) and AI tools, and underscoring the rise of recommender system-based solutions to promote healthier lifestyles across the wider population. The article also discussed ongoing challenges — such as data privacy and model bias — that come with implementing personalized healthcare solutions, putting a final sight at prospects and future directions for continuing innovations in this field.
Predictive and Descriptive Analytics in Personalized Healthcare
Predictive and descriptive analytics are two key elements in personalizing healthcare by transforming raw data into actionable insights. Descriptive analytics methods are used to identify common trends and patterns in historical patient data. Meanwhile, predictive analytics methods focus on forecasting outcomes based on data inputs. Such outcomes range from diagnosis to disease progression, to risk of relapse, among many others. Both forms of data analysis enable healthcare professionals to deliver more targeted care by anticipating patient needs, be it by improving treatment plans or making enhanced decisions. An analytics-driven personalized healthcare experience ultimately yields not only better health outcomes but also patient satisfaction.
Among the technologies that revolutionized the capabilities and expanded the limits of data analytics for personalized healthcare, AI and particularly machine learning stand out. Let's examine their role more closely.
The Role of Machine Learning and Emerging AI Approaches
ML systems used in the health domain enable computers to analyze vast healthcare data, such as patient records or medical images, to learn by themselves to perform accurate predictions, infer valuable knowledge from the data, and make better decisions. Unlike traditional analytics methods, ML models are very effective in uncovering complex patterns and dealing with complex and disparate data sources, improving diagnosis and patient treatment through personalization. ML has undoubtedly transformed healthcare into a more patient-centered and data-driven approach, and the following real-world examples illustrate this phenomenon, outlining a number of use cases, data and ML/AI technologies involved, and the benefits of their use.
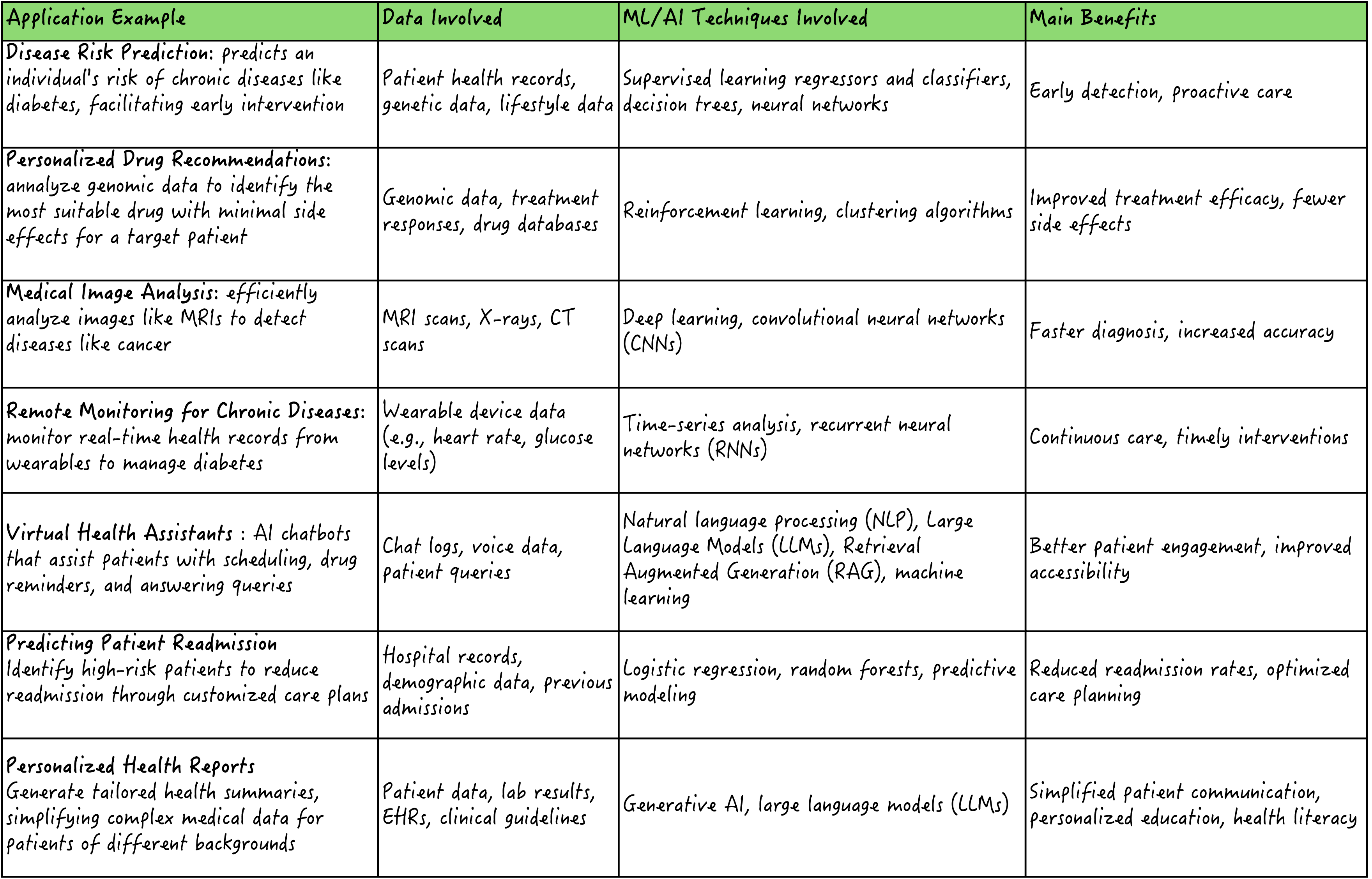
Image by Author (click to enlarge)
From more traditional ML approaches like supervised classification and regression to computer vision and emerging solutions based on blending generative AI and natural language processing, every side of the AI/ML spectrum has a big say in improving healthcare through personalization.
Personalized Well-Being and Lifestyle for Everyone
Recommender systems are a popular application of AI/ML techniques in e-commerce, tourism and entertainment platforms, where products, services, and content are recommended to individual users or customers based on their needs or preferences. One common approach to do this is by using collaborative filtering: recommending what turned out successful or effective on users that are (in terms of data) deemed similar to the target user.
Whilst historically, the field of recommender systems has not been widely applied to the healthcare field, this view has started to change in recent years, with the emergence of recommender system solutions aimed at engaging individuals with a healthier and more balanced lifestyle through personalized suggestions. Just like traditional e-commerce recommender engines analyze user-site interaction patterns, purchase history, and product ratings to find out what users like or need, recommender systems for healthcare focus on analyzing a blend of medical, sensor, and wearable data, as well as log data like daily activity or food diaries to assist patients or the general population in a more tailored manner.
Some trends of research in this direction include:
- Engagement of older adults with an active lifestyle: using recommender systems for fostering responsive engagement of older adults in daily activities, suggesting them daily or weekly exercising routines (link).
- Food recommendation: taking into account food preferences and dietary habits to recommend balanced and appropriate meals for patients suffering from chronic conditions (link).
- Integrated healthy plans: blending food and exercise suggestions by using AI optimization techniques like genetic algorithms on top of recommender approaches to promote healthier living (link).
- Personalized stress management and monitoring: from a mental health perspective, there are studies suggesting the use of personalized recommendations to analyze sleep and heart rate data collected by wearable devices to offer tailored relaxation techniques and lifestyle hacks to reduce stress and anxiety levels (link).
A common trend in these research directions — and personalized healthcare as a whole — is the key role played by wearable devices to collect valuable health data in a non-intrusive and highly effective way.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the progress made in using data science, analytics, and AI approaches in personalized healthcare, some challenges remain at present for fully leveraging their effective and responsible use:
- Data Privacy and Security: healthcare applications involve a considerable deal of sensitive patient data, making the safeguarding of these data and regulatory compliance an extra challenge.
- Data quality and integration: most personalized healthcare use cases become optimal when fueled by diverse types and forms of data. Inconsistent data formats and missing information (often occurring with wearable sensors) can hinder optimal healthcare service delivery.
- Biases: AI/ML systems trained upon biased data (e.g. patient data over-representing a certain ethnic group against others) will likely lead to biased outcomes or decisiones, perpetuating discriminatory actions against underrepresented groups.
Finally, and looking ahead, key areas for future developments and further advances in data-driven personalized healthcare include:
- Cutting-edge AI techniques: integrating more robust models, like federated learning and explainable AI to understand AI outcomes, are key to further enhancing personalization.
- Ethical standards: develop clearer and more domain-specific guidelines for data ownership and use, AI ethics, accountability, and patient consent.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: promoting partnerships between healthcare professionals, technologists, and policy-makers constitutes a promising direction to drive innovation and improve overall healthcare services through personalization and responsible use of AI and data.
Iván Palomares Carrascosa is a leader, writer, speaker, and adviser in AI, machine learning, deep learning & LLMs. He trains and guides others in harnessing AI in the real world.
