How To Fine Tune Your Machine Learning Models To Improve Forecasting Accuracy
We explain how to retrieve estimates of a model's performance using scoring metrics, before taking a look at finding and diagnosing the potential problems of a machine learning algorithm.
Fine tuning machine learning predictive model is a crucial step to improve accuracy of the forecasted results. In the recent past, I have written a number of articles that explain how machine learning works and how to enrich and decompose the feature set to improve accuracy of your machine learning models.
This article discovers details of:
- Retrieving estimates of a model’s performance using scoring metrics
- Finding and diagnosing the common problems of machine learning algorithms
- Fine-tuning parameters of machine learning models
Please read FinTechExplained
disclaimer.
Step 1: Understand what tuning machine learning model is
Sometimes, we have to explore how model parameters can enhance forecasting accuracy of our machine learning model.
Fine tuning machine learning model is a black art. It can turn out to be an exhaustive task. I will be covering a number of methodologies in this article that we can follow to get accurate results in a shorter time.
I am often asked a question on the techniques that can be utilised to tune the forecasting models when the features are stable and the feature set is decomposed. Once everything is tried, we should look to tune our machine learning models.
Tuning Machine Learning Model Is Like Rotating TV Switches and Knobs Until You Get A Clearer Signal
This diagram illustrates how parameters can be dependent on one another.
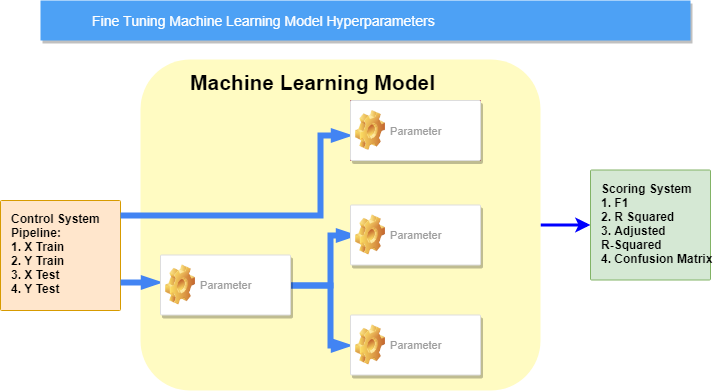
- X Train — Training data of independent variables, also known as features
- X Test — Test data of independent variables
- Y Train — Training data of dependent variable
- Y Test — Test data of dependent variable
For instance, if you are forecasting the volume of waterfall based on the temperature and humidity then the volume of water is represented as Y (dependent variable) and the Temperature and Humidity are the X (independent variables or features). Training data of X is then known as X Train which you can use to train your model.
Hyperparameters are parameters of the models that can be input as arguments to the models.
Step 2: Cover The Basics
Before you fine tune your forecasting model, it is important to briefly understand what machine learning is.
If you are new to machine learning then please have a look at this article:
It is often easier to improve the data that we feed into the models than to fine tune parameters of the model. If you want to improve accuracy of your forecasting model then please enrich data in the feature set first.
If you feed poor quality data in then the model will yield poor results.
Please have a look at this article that highlights common techniques to we can use to enrich the features:
Processing Data To Improve Machine Learning Model Accuracy
If you are unsure whether your model is the most appropriate model for the problem then have a look at this article. It reviews most common algorithms of the machine learning model:
Machine Learning Algorithms Comparison
Step 3: Find Your Score Metric
The most important pre-requisite is to decide on the metric that you are going to use to score the accuracy of the forecasting model.
It could be R squared, Adjusted R squared, Confusion Matrix, F1, Recall, Variance etc.
Read this article to understand the most important mathematical measures that every data scientist should know. These measures are explained in an easy-to-understand manner:
Must Know Mathematical Measures For Every Data Scientist
from sklearn.metrics contains a large number of scoring metrics
Step 4. Obtain Accurate Forecasting Score
Once you have prepared your training set, enriched its features, scaled the data, decomposed the feature sets, decided on the scoring metric and trained your model on the training data then you should test the accuracy of the model on unseen data. The unseen data is known as “test data”.
You can utilise cross validation to assess how your model works on unseen data. This is known as generalisation error of your model.
Cross Validation
There are two common cross validation methodologies
Holdout Cross Validation
It is not a wise machine learning practice to train your model and score its accuracy on the same data set. It is a far superior technique to test your model with varying model parameter values on an unseen test set.
It is a good practice to divide your data set into three parts:
- Training Set
- Validation Set
- Test Set
Train your model on the training set (60% of the data), then perform model selection (tuning parameters) on validation set (20% of the data) and once you are ready, test your model on the test set (20% of the data).
Create your training, validation and test data sets proportions according to the needs of your machine learning model and availability of the data.
K Fold Cross Validation
K-Fold cross validation is a superior mechanism than using holdout cross validation. The way it works is that the data is divided into k folds (parts). k-1 folds are used to train the model and the last fold is used to test the model.
This mechanism is then repeated k times. Furthermore, each time a number of performance metrics can be used to assess and score the performance. The average of the performance metrics are then reported. The class proportions are preserved in StratifiedKFold.
Choose between 8–12 k folds
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score scores = cross_val_score(estimator=pipe_lr, X=X_train, y=Y_train, cv=12, n_jobs=) mean_scores = scores.mean()
n_jobs parameter controls the number of CPUs used to run the cross validation.
Step 5: Diagnose Best Parameter Value Using Validation Curves
Once accurate forecasting scores have been established, find out all of the parameters that your model requires. You can then use validation curves to explore how their values can improve the accuracy of the forecasting models.
Before we tune the parameters, we need to diagnose and find if the model is suffering from under or overfitting.
Models that have a large number of parameters tends to overfit. We can use validation curves to resolve the issue of overfitting and underfitting in machine learning.
The parameters are also known as hyperparameters
Photo by Dominik Scythe on Unsplash
Validation curve is utilised to pass in a range of values for model parameters. It changes the values of the model parameters one at a time and then the accuracy values can be plotted against the model parameter value to assess the accuracy of the model.
For example, if your model takes a parameter named “number of trees” then you can test your model by passing in 10 different values of the parameter. You can use validation curve to report accuracy on each of the parameter value to assess the accuracy. Finally take the score that returns highest accuracy and gives you your required results within acceptable times.
Sci-kit learn offers validation curve module:
from sklearn.learning_curve import validation_curve number_of_trees= [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,99,1000] train_scores, test_scores = validation_curve(estimator=, … X=X_train,y=Y_train, param_range=number_of_trees, …)
Step 6: Use Grid Search To Optimise Hyperparameter Combination
Once we have retrieved optimum values of individual model parameters then we can use grid search to obtain combination of hyperparameter values of a model that can give us the highest accuracy.
Grid Search evaluates all possible combinations of the parameter values.
Grid Search is exhaustive and uses brute-force to evaluate the most accurate values. Therefore it is computationally intensive task.
Use GridSearchCV of sci-kit learn to perform grid search
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
Step 7: Continuously Tune The Parameters To Further Improve Accuracy
The key here is to always enhance the training set as soon as more data is available.
Always test your forecasting model on richer test data that the model has not seen before.
Always ensure that the right model and parameter values are chosen for the job.
It is important to feed more data as soon as it is available and test the accuracy of the model on continuous basis so that the performance and accuracy can be further optimised.
Summary
This article discovered details of how we can:
- Retrieve estimates of a model’s performance using scoring metrics
- Find and diagnose the common problems of machine learning algorithms
- Fine-tune parameters of machine learning models to further enhance the accuracy
Hope it helps.
Original. Reposted with permission.
Resources:
- On-line and web-based: Analytics, Data Mining, Data Science, Machine Learning education
- Software for Analytics, Data Science, Data Mining, and Machine Learning
Related:

