
Matrix Multiplication for Data Science (or Machine Learning)
Learn the math behind matrix multiplication for data science and machine learning with code examples.
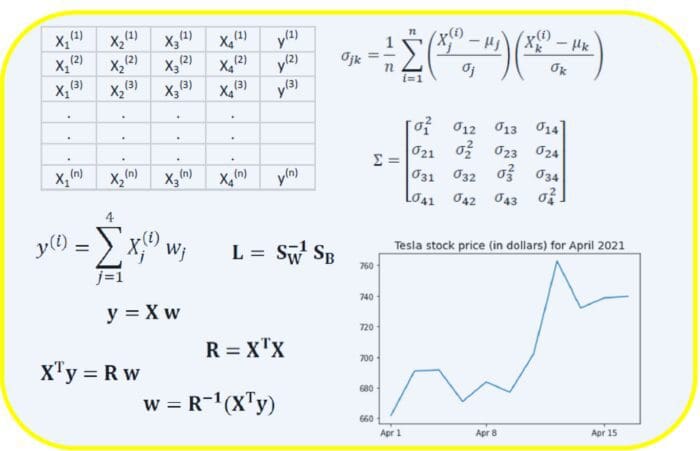
Image by Author
Key Takeaways
- Matrix multiplication plays an important role in data science and machine learning
- For matrix multiplication between two matrices to be well defined, the two matrices must be compatible, that is, the number of columns of matrix A must be equal to the number of rows of matrix B.
- Matrix multiplication is not commutative, that is AB = BA.
Matrix multiplication plays an important role in data science and machine learning. Consider a dataset with m features and n observations as shown below:
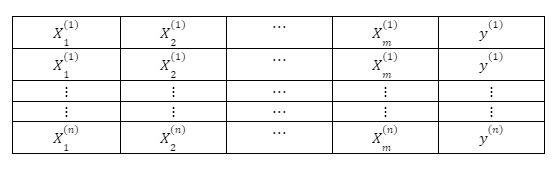
A basic regression model can be represented as follows:
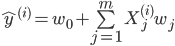
Where is the n×m feature matrix, and w is the m×1 weight coefficients or regression coefficients matrix. Here we observe that the calculation of
involves matrix multiplication between the feature matrix X and the regression coefficient matrix w. Since X is an n ×m matrix and w is an m ×1 matrix, matrix multiplication between X and w is well defined. In matrix form, the equation above can be expressed simply as
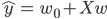
where Xw represents matrix multiplication between X and w.
Definition of Matrix Multiplication
Let A be and n×p matrix, and B a p×m matrix,
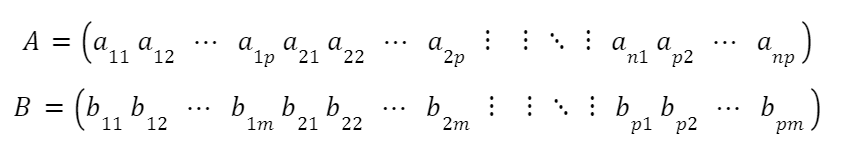
the product matrix C = AB is an n×m matrix with elements given as
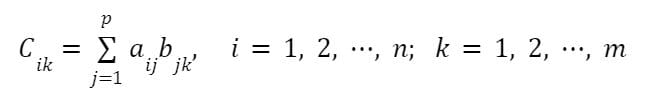
Properties of Matrix Multiplication
Matrix multiplication is not commutative, that is
AB≠BA
Implementation of Matrix Multiplication in Python
Using for Loop
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) # create (2 x 3) matrix
B = np.array([[7,8],[9,10],[11,12]]) # create (3 x 2) matrix
A.shape[1] == B.shape[0] # ensures two matrices are compatible
C = np.zeros((2,2)) # (2 x 2) matrix
for i in range(2):
for k in range(2):
for j in range(3):
C[i,k]= C[i,k] + A[i,j]*B[j,k]
print(C)
[[ 58, 64] [139, 154]]
Using Numpy Library
C = np.dot(A, B)
print(C)
[[ 58, 64] [139, 154]]
Note that np.dot(B, A) gives the following output:
print(np.dot(B, A))
[[ 39 54 69] [ 49 68 87] [ 59 82 105]]
Clearly, we see that np.dot(A, B) ≠ np.dot(B, A).
In summary, we’ve discussed the mathematical basis of matrix multiplication. We also demonstrated how matrix multiplication can be performed using a short python code, and using the in-built matrix multiplication method in numpy.
Benjamin O. Tayo is a Physicist, Data Science Educator, and Writer, as well as the Owner of DataScienceHub. Previously, Benjamin was teaching Engineering and Physics at U. of Central Oklahoma, Grand Canyon U., and Pittsburgh State U.
