Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Computing
Learn how cloud computing works, different types of models, top cloud platforms, and applications.
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, Software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet ("the cloud") to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Organizations can better align IT resources with business objectives and initiatives with cloud computing. Cloud services are often delivered through a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing model, making it more cost-effective and flexible than traditional on-premises IT solutions.

Image by storyset on Freepik
History of Cloud Computing
The term "cloud computing" has only been around for a few years, but the concept has been around for much longer. The idea of using remote servers to store and process data dates back to the 1950s when scientists working on the SAGE air defense system used an early form of cloud computing to share data and resources. In the 1980s and 1990s, companies like CompuServe and AOL began offering their customers essential cloud-based services like email and file storage.
It wasn't until the early 2000s that the term "cloud computing" became widely used. In 2006, Amazon launched its EC2 service, which allowed businesses to rent virtual servers in the company's data centers. It was a significant turning point for the cloud computing industry, demonstrating that the cloud could be used for more than just simple web-based services.
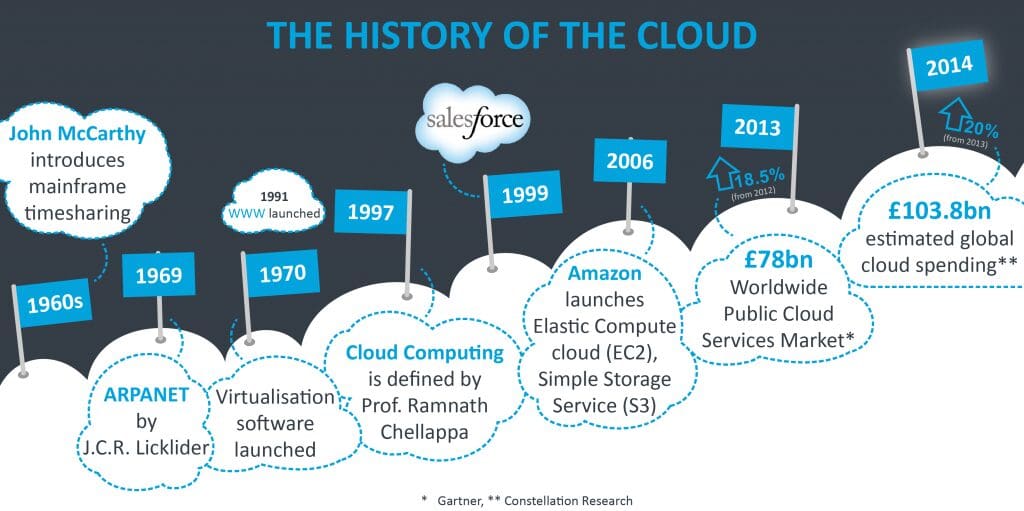
Image by cloudcomputing521
How does Cloud Computing work
Internet-based cloud computing delivers data and shared computing resources on demand to computers and other devices. It is a design that makes it possible for anybody, anywhere, to have easy, anytime access to adjustable computer resources through the network (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services). With little administration work or service provider contact, these resources may be quickly supplied and released. Like a public utility, cloud computing depends on sharing resources to create coherence and economies of scale.
Characteristics
- On-demand self-service: Without contacting each service provider individually, a customer may automatically independently provide necessary computer resources, such as server time and network storage.
- Wide-ranging network access: Capabilities are accessible via the network and accessed via standard procedures to encourage usage by various thin- or thick-client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, and PDAs).
- Resource pooling: Using a multi-tenant approach, the provider's computer resources are combined to serve several customers. According to customer demand, various physical and virtual resources are constantly assigned and reassigned.
- Scalability: It is one of the most significant advantages of cloud computing. With on-demand resources, businesses can quickly scale up or down as needed without making any upfront investments.
- Flexibility: Cloud Computing is very flexible in payment options. With a pay-as-you-go model, businesses only pay for the resources they use when they use them. This can be a great way to save on costs, as companies can avoid overpaying for help they don't need.
- Cost-effectiveness: You can save much money compared to traditional IT infrastructure by only paying for the resources you use. In addition, many cloud providers offer discounts for longer-term contracts, making them even more affordable.
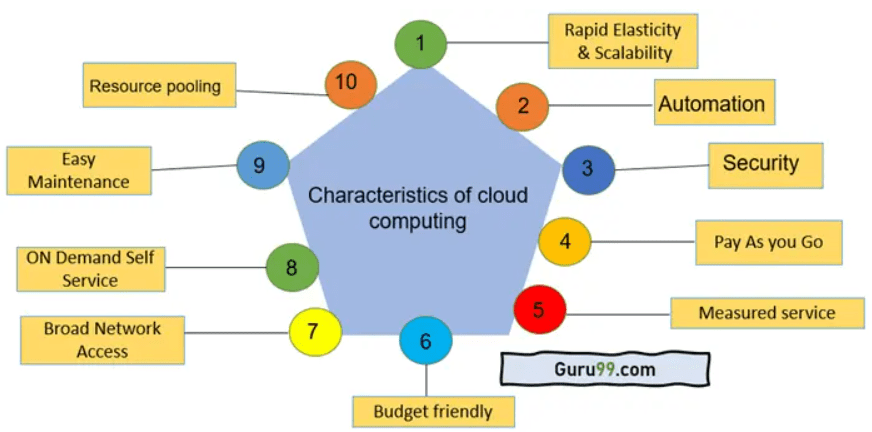
Image by guru99
Services of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing services come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Here are some of the most popular types of services that are available:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider delivers computer infrastructure—typically a platform virtualization environment—as a service. IaaS is one of three main categories of cloud services, alongside Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
IaaS providers offer customers a pay-as-you-go model for using, managing, and scaling infrastructure resources, including storage, networking, and computing power. Customers can access these resources on-demand and only pay for the resources they use.
IaaS is a popular choice for businesses that want the flexibility and scalability of the cloud without the need to manage and maintain their Infrastructure. IaaS providers typically offer a wide range of services, which can be customized to meet the needs of each customer.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
In cloud computing, Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a type of service that provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. The Platform can be used to create or run new applications. Developers typically use PaaS services to build and test applications before deploying them to a production environment.
PaaS solutions are typically delivered as a cloud service, meaning that they are available over the Internet and can be accessed by users from anywhere. PaaS providers usually manage the Infrastructure and Platform for their customers, freeing up developers to focus on building and managing applications.
PaaS solutions can include many features and services, from development tools and frameworks to application management and monitoring. Some PaaS solutions also offer features for scaling applications and integrating with other cloud services.
PaaS services can be used to develop and deploy a wide range of applications, from simple websites to complex data-driven applications.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) is a type of cloud computing that delivers Software over the Internet. SaaS is a way for businesses to access Software in the cloud without having to install and run it on their computers.
SaaS applications are typically accessed via a web browser, while the Software and data are stored on the cloud provider's servers. SaaS is a subscription-based model that allows businesses to pay for only the Software they use on a monthly or annual basis.
SaaS applications are typically more straightforward to use than traditional on-premises Software, as they are designed for a wide range of users and don't require extensive training. They are also more affordable, as businesses only pay for what they use.
SaaS applications can be used for various tasks, such as CRM, project management, invoicing, and accounting.
4. Storage as a Service (STaaS)
Storage as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud storage model that provides users access to their data and files over the Internet. SaaS providers typically offer a variety of storage plans and pricing options, making it easy for users to find a storage solution that fits their needs. While STaaS providers usually manage and maintain the storage infrastructure, users are responsible for their data and files. STaaS providers typically offer a variety of features and tools to help users manage their data and files, including access control, data encryption, and versioning.
5. Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Backup as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based backup solution that helps organizations to protect their data and ensure business continuity. It offers a pay-as-you-go model that is flexible and scalable, making it ideal for businesses of all sizes.
BaaS provides several benefits, including:
- Reduced costs: BaaS is a cost-effective solution as it eliminates the need for expensive on-premise backup Infrastructure.
- Increased agility: BaaS enables organizations to be more agile as they can quickly scale up or down their backup storage capacity as required.
- Improved security: BaaS provides enhanced security as data is stored off-site in a secure cloud environment.
- Enhanced reliability: BaaS is a reliable solution provided by leading cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
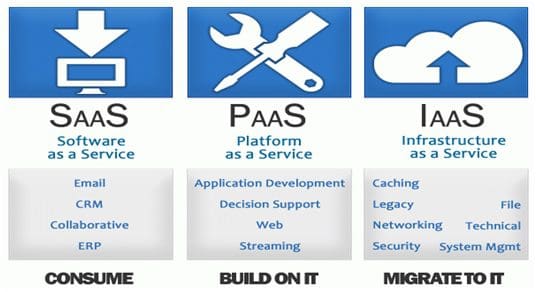
Image by includehelp
Models of Cloud Computing
Three types of cloud computing models exist private, public, and hybrid. Each has its advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before implementation.
Public Cloud
Public cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Public cloud services are provided by third-party providers and delivered over the Internet.
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from public cloud computing as it can help them save on IT infrastructure and maintenance costs. In addition, public cloud computing can help businesses improve their agility and scalability.
There are several public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Businesses can select the provider that best meets their needs.
There are a few disadvantages of public cloud computing that are worth mentioning.
- Public clouds are often less secure than private clouds. This is because public clouds are shared among many users, which can make it difficult to control access and prevent data breaches.
- Public clouds can be less reliable than private clouds since they are subject to the whims of the Internet. If the Internet goes down, so does your public cloud.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a type of cloud computing that delivers similar advantages to the public cloud, including scalability and self-service, but through a proprietary architecture. Private clouds can be deployed on-premises, off-premises, or a hybrid of both.
Advantages
- Increased control and security: Since private clouds are deployed on a company's premises, they offer greater control and security than public clouds. Private clouds can be customized to a company's specific needs and integrated with its security infrastructure.
- Greater scalability and flexibility: Private clouds can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing needs. They can also be more flexible than public clouds since they can be customized to a company's specific needs.
- Lower costs: Private clouds can be more cost-effective than public clouds since they don't require the same investment in Infrastructure.
Disadvantages
Businesses should be aware of a few disadvantages of private cloud computing before switching. One of the most significant disadvantages is the cost. Private clouds can be expensive to set up and maintain, especially if you need to hire experts to manage them. Another disadvantage is that private clouds can be complex to set up and work with, and finding the right mix of features and services that meet your specific needs can be challenging. Finally, private clouds can be less flexible than public clouds, and you may have to make some sacrifices in terms of features and services to get the most out of your private cloud.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud in computing comprises two or more clouds (private, public, or community) that are still separate but linked together to provide the advantages of various deployment types. A hybrid cloud service transcends provider and isolation barriers, making it impossible to lock it inside a single cloud vendor.
The essential characteristic of a hybrid cloud is the ability to connect disparate cloud services, usually through network-based integration, to work as a single entity. The integration can be done in several ways, but the most common is via a virtual private network (VPN) or a private network connection.
The main benefit of a hybrid cloud is combining the best of both worlds: the public cloud's scalability and cost-effectiveness with the private cloud's security and control. This can give your organization the agility and flexibility to respond quickly to market changes without sacrificing the security and compliance of your most sensitive data.
Disadvantages
There are a few disadvantages of hybrid cloud computing to consider before implementing this type of solution for your business. One disadvantage is the increased complexity of managing both on-premise and cloud-based resources. This can make it more difficult to troubleshoot issues and keep track of changes to your environment.
Another potential disadvantage is the cost. While the hybrid cloud can provide some cost savings by leveraging the economies of scale of the public cloud, you may still incur additional charges for managing and integrating your on-premise and cloud-based resources.
Finally, security can be a concern with a hybrid cloud. It is essential to carefully consider how you will secure data and access your on-premise and cloud-based resources.
Despite these potential disadvantages, a hybrid cloud can be a very effective solution for many businesses. Carefully weigh the pros and cons to determine if the hybrid cloud is the right solution for your organization.
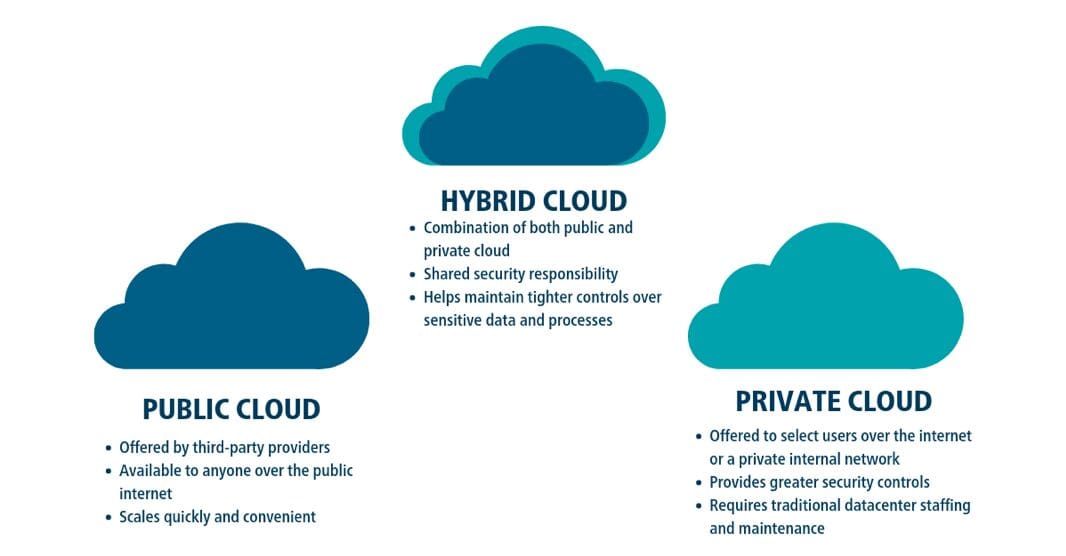
Image by karansinghreen
Famous Platforms for Cloud Computing
There are many famous platforms for cloud computing, but some of the most popular are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. Each of these platforms offers various services that can be used to build, deploy, and scale applications. They also provide different pricing options to choose the best fit for your needs.
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS offers various services to help businesses move faster, lower IT costs, and scale. Here are some of the most popular services provided by AWS:
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): EC2 is a web-based service that allows businesses to rent virtual machines (VMs) that they can use to run applications and store data.
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3): S3 is an object storage service that businesses can use to store and retrieve any amount of data anywhere on the web.
- Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS): RDS is a managed relational database service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud.
- Amazon CloudFront: CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) that speeds up the delivery of static and dynamic web content to users worldwide.
2. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform offers a variety of services to help businesses succeed. There's a lot to choose from, from computing and storage to big data and machine learning. But which services are right for your business?
Here's a quick overview of some of the most popular services offered by the Google Cloud Platform:
- Compute Engine: A robust and scalable cloud computing platform that can handle any workload.
- Storage: A reliable and cost-effective storage solution for your data, with block and object storage options.
- BigQuery: A fast, powerful, and cost-effective big data analytics platform.
- Cloud SQL: A fully managed relational database service for your data.
- Cloud Spanner: A globally distributed database service for mission-critical workloads.
- Machine Learning: A suite of robust machine learning services that can help you train models and make predictions.
And these are just a few of the many services the Google Cloud Platform offers.
3. Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure offers a variety of services that can be used to build, deploy, and manage applications. These services include:
- Azure Compute: This service provides the ability to create and manage virtual machines and deploy and manage containers.
- Azure Storage: This service provides the ability to create and manage storage accounts, as well as blob, queue, and table storage.
- Azure Networking: This service can create and manage virtual networks, load balancers, and DNS.
- Azure Security: This service can create and manage security groups and access control lists.
- Azure Monitor: This service can collect and analyze diagnostic data.
- Azure Active Directory: This service can create and manage Azure Active Directory accounts.

Image by allcode
Applications of Cloud Computing
There are many different applications for cloud computing, which is why this technology has become so popular in recent years. Here are some of the most common applications for cloud computing:
1. Storage
Cloud storage is a great way to store data off-site and have it accessible from anywhere. This can be useful for businesses that want to keep backups of their data in case of a disaster or individuals who want to store photos and videos securely online.
2. Computing
Cloud computing can be used for anything from running a website to powering complex applications. Businesses can save money on expensive hardware and software licenses by using cloud resources
3. Collaboration
Cloud-based applications make it easy for team members to collaborate on projects from anywhere in the world. This can be a considerable time and money saver for businesses with employees who work remotely.
4. Ecommerce
Cloud computing is revolutionizing the e-commerce industry. By making it possible to connect to the internet and store data in the cloud, businesses can operate more efficiently and scale more quickly.
There are many ways cloud computing can be used in e-commerce. One of the most popular is using a cloud-based platform to build and host an online store. This can be an excellent option for businesses that want to launch an eCommerce store quickly and without a significant upfront investment.
Another way cloud computing can be used in eCommerce is through cloud-based applications. These can streamline various aspects of an online store, such as inventory management, order processing, and customer service.
Finally, cloud computing can also store and manage customer data. This can be a valuable tool for businesses that want to understand their customers better and provide them with personalised service.
5. Education
Cloud computing is transforming education. It offers new possibilities for teaching, learning, and research. It provides access to a vast pool of resources and services. And it allows educators and learners to connect and collaborate in new ways.
The use of cloud computing in education is still in its early stages, but its potential is already evident. Here are some ways in which cloud computing is being used in education today:
- Online learning: Cloud computing is playing a significant role in the growth of online learning. Online courses and programs are now more accessible than ever before. And the use of cloud-based learning management systems (LMS) is making it easier for educators to create and deliver online courses.
- Collaborative learning: Cloud computing makes it easier for students to collaborate on projects and assignments. With cloud-based tools, students can work together on documents, presentations, and other files in real-time.
6. Antivirus
One of the most exciting applications of cloud computing is in the area of antivirus. Antivirus software has traditionally been installed on individual computers, and each would need to be updated with the latest virus definitions to be protected.
With cloud-based antivirus, the virus definitions are stored in the cloud, and each computer connected to the internet can access them. This means that all your computers can be protected without you having to worry about updating each one individually.
Cloud-based antivirus is also more effective at detecting and removing viruses because the cloud-based system can analyze a more significant number of samples and can quickly identify new threats.
7. GPS(Global Positioning System)
GPS tracking is a location-based service that uses satellite navigation to track the location of assets and people. It is often used by businesses to track the location of vehicles, fleets, and other equipment. GPS tracking can also be used for personal tracking applications, such as monitoring children or elderly family members.
Using GPS tracking in conjunction with cloud computing is a powerful combination that can offer many benefits. Cloud-based GPS tracking systems can provide real-time tracking data that can be accessed from any internet-connected device. This allows businesses to track their assets and people in real-time, no matter where they are.
Cloud-based GPS tracking systems can also offer features that are not possible with traditional GPS tracking systems. For example, some cloud-based systems allow businesses to set up virtual fences around their assets. If an asset crosses the virtual wall, the company is immediately notified. This can be a valuable security feature that can help businesses protect their investments.
Image by guru99
Conclusion
The demand for cloud computing services will only grow as the world becomes increasingly digitized. Here are a few predictions for the future of cloud computing:
- The cloud will become more ubiquitous: More and more businesses and individuals will rely on cloud-based services to get work done.
- The cloud will become more intelligent: With the help of artificial intelligence, the cloud will become better at meeting users' needs.
- The cloud will become more secure: As security concerns continue to increase, cloud providers will invest more in security features and technologies.
- The cloud will become more affordable: As the demand for cloud services grows, providers will compete on price, making cloud-based services more affordable for everyone.
- The cloud will become more flexible: With the rise of containerization and serverless computing, the cloud will become even more flexible and scalable.
The future market size of cloud computing is expected to be huge. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global cloud computing market is expected to reach $623.3 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud services by small and medium businesses, the growing need for cost-effective and scalable computing solutions, and the increasing popularity of cloud-based applications.
Key takeaways of this article
- Firstly, we have discussed cloud computing and its history. Also discussed are its significant characteristics like cost effectiveness, scalability, etc.
- After that, we discussed various services offered like (PaaS, IaaS, SaaS, etc.)
- Then we have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of various cloud computing models like Private Cloud, Public Cloud & Hybrid Cloud.
- Finally, we have discussed the various companies like Google and Microsoft, which offer resources for cloud computing. And then concluded the article by discussing the future of cloud computing.
That's all for now. I trust you liked reading the post. Please leave a remark below if you have any questions or ideas.
Aryan Garg is a B.Tech. Electrical Engineering student, currently in the final year of his undergrad. His interest lies in the field of Web Development and Machine Learning. He have pursued this interest and am eager to work more in these directions.
