Natural Language Processing Key Terms, Explained
This post provides a concise overview of 18 natural language processing terms, intended as an entry point for the beginner looking for some orientation on the topic.

Photo by Towfiqu barbhuiya on Unsplash
At the intersection of computational linguistics and artificial intelligence is where we find natural language processing. Very broadly, natural language processing (NLP) is a discipline which is interested in how human languages, and, to some extent, the humans who speak them, interact with technology. NLP is an interdisciplinary topic which has historically been the equal domain of artificial intelligence researchers and linguistics alike; perhaps obviously, those approaching the discipline from the linguistics side must get up to speed on technology, while those entering the discipline from the technology realm need to learn the linguistic concepts.
It is this second group that this post aims to serve at an introductory level, as we take a no-nonsense approach to defining some key NLP terminology. While you certainly won't be a linguistic expert after reading this, we hope that you are better able to understand some of the NLP-related discourse, and gain perspective as to how to proceed with learning more on the topics herein.
So here they are, 18 select natural language processing terms, concisely defined.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) concerns itself with the interaction between natural human languages and computing devices. NLP is a major aspect of computational linguistics, and also falls within the realms of computer science and artificial intelligence.
2. Tokenization
Tokenization is, generally, an early step in the NLP process, a step which splits longer strings of text into smaller pieces, or tokens. Larger chunks of text can be tokenized into sentences, sentences can be tokenized into words, etc. Further processing is generally performed after a piece of text has been appropriately tokenized.
3. Normalization
Before further processing, text needs to be normalized. Normalization generally refers to a series of related tasks meant to put all text on a level playing field: converting all text to the same case (upper or lower), removing punctuation, expanding contractions, converting numbers to their word equivalents, and so on. Normalization puts all words on equal footing, and allows processing to proceed uniformly.
4. Stemming
Stemming is the process of eliminating affixes (suffixed, prefixes, infixes, circumfixes) from a word in order to obtain a word stem.
5. Lemmatization
Lemmatization is related to stemming, differing in that lemmatization is able to capture canonical forms based on a word's lemma.
For example, stemming the word "better" would fail to return its citation form (another word for lemma); however, lemmatization would result in the following:
It should be easy to see why the implementation of a stemmer would be the less difficult feat of the two.
6. Corpus
In linguistics and NLP, corpus (literally Latin for body) refers to a collection of texts. Such collections may be formed of a single language of texts, or can span multiple languages -- there are numerous reasons for which multilingual corpora (the plural of corpus) may be useful. Corpora may also consist of themed texts (historical, Biblical, etc.). Corpora are generally solely used for statistical linguistic analysis and hypothesis testing.
7. Stop Words
Stop words are those words which are filtered out before further processing of text, since these words contribute little to overall meaning, given that they are generally the most common words in a language. For instance, "the," "and," and "a," while all required words in a particular passage, don't generally contribute greatly to one's understanding of content. As a simple example, the following panagram is just as legible if the stop words are removed:
8. Parts-of-speech (POS) Tagging
POS tagging consists of assigning a category tag to the tokenized parts of a sentence. The most popular POS tagging would be identifying words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.
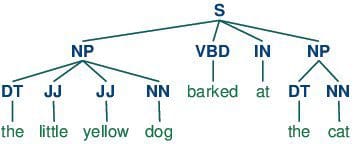
9. Statistical Language Modeling
Statistical Language Modeling is the process of building a statistical language model which is meant to provide an estimate of a natural language. For a sequence of input words, the model would assign a probability to the entire sequence, which contributes to the estimated likelihood of various possible sequences. This can be especially useful for NLP applications which generate text.
10. Bag of Words
Bag of words is a particular representation model used to simplify the contents of a selection of text. The bag of words model omits grammar and word order, but is interested in the number of occurrences of words within the text. The ultimate representation of the text selection is that of a bag of words (bag referring to the set theory concept of multisets, which differ from simple sets).
Actual storage mechanisms for the bag of words representation can vary, but the following is a simple example using a dictionary for intuitiveness. Sample text:
"There, there," said James. "There, there."
The resulting bag of words representation as a dictionary:
{
'well': 3,
'said': 2,
'john': 1,
'there': 4,
'james': 1
}
11. n-grams
n-grams is another representation model for simplifying text selection contents. As opposed to the orderless representation of bag of words, n-grams modeling is interested in preserving contiguous sequences of N items from the text selection.
An example of trigram (3-gram) model of the second sentence of the above example ("There, there," said James. "There, there.") appears as a list representation below:
[
"there there said",
"there said james",
"said james there",
"james there there",
]
12. Regular Expressions
Regular expressions, often abbreviated regexp or regexp, are a tried and true method of concisely describing patterns of text. A regular expression is represented as a special text string itself, and is meant for developing search patterns on selections of text. Regular expressions can be thought of as an expanded set of rules beyond the wildcard characters of ? and *. Though often cited as frustrating to learn, regular expressions are incredibly powerful text searching tools.
13. Zipf's Law
Zipf's Law is used to describe the relationship between word frequencies in document collections. If a document collection's words are ordered by frequency, and y is used to describe the number of times that the xth word appears, Zipf's observation is concisely captured as y = cx-1/2 (item frequency is inversely proportional to item rank). More generally, Wikipedia says:
Zipf's law states that given some corpus of natural language utterances, the frequency of any word is inversely proportional to its rank in the frequency table. Thus the most frequent word will occur approximately twice as often as the second most frequent word, three times as often as the third most frequent word, etc.
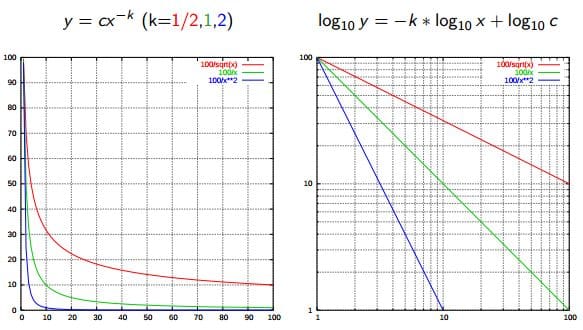
Source: Wikipedia
14. Similarity Measures
There are numerous similarity measures which can be applied to NLP. What are we measuring the similarity of? Generally, strings.
- Levenshtein - the number of characters that must be deleted, inserted, or substituted in order to make a pair of strings equal
- Jaccard - the measure of overlap between 2 sets; in the case of NLP, generally, documents are sets of words
- Smith Waterman - similar to Levenshtein, but with costs assigned to substitution, insertion, and deletion
15. Syntactic Analysis
Also referred to as parsing, syntactic analysis is the task of analyzing strings as symbols, and ensuring their conformance to a established set of grammatical rules. This step must, out of necessity, come before any further analysis which attempts to extract insight from text -- semantic, sentiment, etc. -- treating it as something beyond symbols.
16. Semantic Analysis
Also known as meaning generation, semantic analysis is interested in determining the meaning of text selections (either character or word sequences). After an input selection of text is read and parsed (analyzed syntactically), the text selection can then be interpreted for meaning. Simply put, syntactic analysis is concerned with what words a text selection was made up of, while semantic analysis wants to know what the collection of words actually means. The topic of semantic analysis is both broad and deep, with a wide variety of tools and techniques at the researcher's disposal.
17. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is the process of evaluating and determining the sentiment captured in a selection of text, with sentiment defined as feeling or emotion. This sentiment can be simply positive (happy), negative (sad or angry), or neutral, or can be some more precise measurement along a scale, with neutral in the middle, and positive and negative increasing in either direction.
18. Information Retrieval
Information retrieval is the process of accessing and retrieving the most appropriate information from text based on a particular query, using context-based indexing or metadata. One of the most famous examples of information retrieval would be Google Search.
Matthew Mayo (@mattmayo13) is a Data Scientist and the Editor-in-Chief of KDnuggets, the seminal online Data Science and Machine Learning resource. His interests lie in natural language processing, algorithm design and optimization, unsupervised learning, neural networks, and automated approaches to machine learning. Matthew holds a Master's degree in computer science and a graduate diploma in data mining. He can be reached at editor1 at kdnuggets[dot]com.
